combinat::skewPartitions – skew partitions
The library combinat::skewPartitions provides functions for counting, generating, and manipulating skew partitions of fixed size.
→ Examples
Superdomain
Dom::BaseDomain
Categories
Cat::CombinatorialClass
Axioms
Ax::systemRep
Related Domains:
combinat::partitions
Details:
-
A skew partition  of size
of size 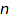 is a pair of two partitions
is a pair of two partitions  where
where  is a partition of the integer
is a partition of the integer 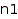 ,
,  is a partition of the integer
is a partition of the integer  ,
,  is an inner partition of
is an inner partition of 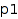 and
and  . We say that
. We say that  and
and  are respectively the outer and inner partitions of
are respectively the outer and inner partitions of 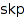 .
.
-
A skew partition is so represented in MuPAD by a list of two partitions:
[outer, inner].
-
A skew partition can be depicted by a diagram made of rows of boxes, in the same way as a partition. Only the boxes of the outer partition  which are not in the inner partition
which are not in the inner partition  appear in the picture. For example, this is the diagram of the skew partition [[5,4,3,1],[3,3,1]]:
appear in the picture. For example, this is the diagram of the skew partition [[5,4,3,1],[3,3,1]]:
+---+
| |
+---+---+---+
| | |
+---+---+---+
| |
+---+---+
| | |
+---+---+
And this is not a skew partition:
+---+
| |
+---+---+---+
| | |
+---+---+
+---+---+
| | |
+---+---+
-
A skew partition can be connected, which can be easily described in graphic terms: for each pair of consecutive rows, there are at least two boxes (one in each row) which have a common edge. This is the the diagram of the connected skew partition [[5,4,3,1],[3,1]]:
+---+
| |
+---+---+---+
| | |
+---+---+---+
| | | |
+---+---+---+---+
| | |
+---+---+
And our first example of skew partition is not a connected one.
-
To apply a reflection w.r.t. the main diagonal to the diagram yields the diagram of the conjugate skew partition, here [[4,3,3,2,1],[3,2,2]]:
+---+
| |
+---+---+---+
| | |
+---+---+---+
| |
+---+
| |
+---+---+
| |
+---+
See combinat::skewPartitions::conjugate.
-
The outer corners of a skew partition are the corners of its outer partition. The inner corners are the internal corners of the outer partition when the inner partition is taken off. See the examples below.
Entries
|
"domtype"
|
The MuPAD domain of skew partitions: DOM_LIST
|
|
"typeConnected"
|
The MuPAD type of connected skew partitions.
|
isA – test if a object is a skew partition
combinat::skewPartitions::isA(any type  , <nonnegative integer n, <Connected>>)
, <nonnegative integer n, <Connected>>)
Tests whether skp is a skew partition. The second argument is either Connectedor a non negative integer. In the case it is a non negative integer, it indicates the size of the skew partition and the function tests if skp is a skew partition of size n, and if it is Connectedthe function tests whether skp is a connected skew partition. With three arguments it is possible to tests if skp is a connected skew partition of size n.
count – number of skew partitions
combinat::skewPartitions::count(nonnegative integer 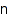 , <Connected>)
, <Connected>)
Returns the number of skew partitions of size n. The result counts only the connected skew partitions if it is said so.
generator – generator for skew partitions
combinat::skewPartitions::generator(nonnegative integer  , <Connected>)
, <Connected>)
Returns a generator for the skew partitions of size n. The result gives access only to connected skew partitions if it is said so.
list – list of skew partitions
combinat::skewPartitions::list(nonnegative integer 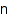 , <Connected>)
, <Connected>)
Returns the list of the skew partitions of size n. The result is a list of connected skew partitions if it is said so.
conjugate – conjugate of a skew partition
combinat::skewPartitions::conjugate(skew partition skp)
Returns the conjugate (or transposed) of the skew partition skp. Geometrically, this operation amounts to a reflection of the diagram of the partition with respect to the main diagonal.
rowLengths – row-lengths of skew partition
combinat::skewPartitions::rowLengths(skew partition skp)
Returns the row-lengths that is the list of the numbers of boxes in each rows of the skew partition skp, starting with the bottom row.
columnLengths – column-lengths of skew partition
combinat::skewPartitions::columnLengths(skew partition skp)
Returns the column-lengths that is the list of the numbers of boxes in each columns of the skew partition skp.
fromRowAndColumnLengths – retrieve a skew partition from it row and column-lengths
combinat::skewPartitions::fromRowAndColumnLengths(composition rowL, composition colL)
Returns the skew-partitions whose row and column-lengths are rowL and colL, returns FAIL if there is no such skew-partitions.
jacobiTrudy – Jacoby-Trudi formula
combinat::skewPartitions::jacobiTrudy(skew partition 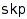 , <function f>, <domain coeffRing>)
, <function f>, <domain coeffRing>)
This function compute the Jacobi-Trudy matrix associated to the skew partition skp. Its determinant express the skew Schur polynomial associated to skp on the basis of homogenous complete symmetric polynomial (see Macdonald I.-G., (1995), "Symmetric Functions and Hall Polynomials", Oxford Science Publication). By default the function argument is i -> h[i] and coeffRing is Dom::ExpressionField() . These two options permits to obtain matrix entries as true symmetric functions.
innerCorners – inner corners of a skew partition
combinat::skewPartitions::innerCorners(skew partition skp)
Returns the list of coordinates of the inner corner boxes in the diagram of the skew partition.
outerCorners – outer corners of a skew partition
combinat::skewPartitions::outerCorners(skew partition skp)
Returns the list of coordinates of the outer corner boxes in the diagram of the skew partition, i.e. the corners of the outer partition of skp.
printPretty – graphic representation of a skew partition
combinat::skewPartitions::printPretty(skew partition skp)
Returns a graphic representation of the skew partition as rows of boxes.
printCompact – graphic representation of a skew partition
combinat::skewPartitions::printCompact(skew partition skp)
Same as above, but in a more compact way, where each box is represented by #.
printPrettyCorners – graphic representation of inner and outer corners of a skew partition
combinat::skewPartitions::printPrettyCorners(skew partition skp)
Returns a graphic representation of the skew partition as rows of boxes where inner corners are marked with x and outer corners are marked with *. A % marks a corner which is inner and outer at the same time.
printCompactCorners – graphic representation of inner and outer corners of a skew partition
combinat::skewPartitions::printCompactCorners(skew partition skp)
Same as above, but in a more compact way, where each box is represented by #, and x, *, % mark the corners.
Example 1:
There are 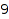 skew partitions of size
skew partitions of size  :
:
combinat::skewPartitions::count(3)

Here is the list:
combinat::skewPartitions::list(3)

Here is a graphic representation of the list:
map(combinat::skewPartitions::list(3),
combinat::skewPartitions::printCompact)
-- # # ## ## # # # # --
| ###, ##, ##, #, #, #, #, # , # |
-- # # # # --
There are 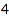 connected skew partitions of size
connected skew partitions of size 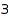 :
:
combinat::skewPartitions::count(3, Connected)

Here is the list:
combinat::skewPartitions::list(3, Connected)

Here is a graphic representation of the list:
map(combinat::skewPartitions::list(3, Connected),
combinat::skewPartitions::printPretty)
-- +---+ --
| | | |
| +---+ +---+---+ +---+ |
| | | | | | | | |
| +---+---+---+ +---+---+ +---+---+ +---+ |
| | | | |, | | |, | |, | | |
-- +---+---+---+ +---+---+ +---+ +---+ --
When you want to run through the skew partitions of a given size, you can generate them one by one to save memory:
g := combinat::skewPartitions::generator(3):
g(); g(); g(); g(); g(); g(); g(); g(); g(); g()


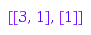

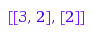



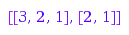

It is also possible to generate connected skew partitions of a given size:
g := combinat::skewPartitions::generator(3, Connected):
g(); g(); g(); g(); g()


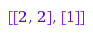
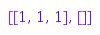

Typically, this would be used as follows:
g := combinat::skewPartitions::generator(3, Connected):
while (p := g()) <> FAIL do print(p): end:
[[3], []]
[[2, 1], []]
[[2, 2], [1]]
[[1, 1, 1], []]
Example 2:
This is the conjugate of the skew partition [[4, 3, 1], [2]]:
combinat::skewPartitions::conjugate([[4, 3, 1], [2]])
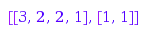
Geometrically, we just applied a reflection with respect to the main diagonal on the diagram of the partition. Of course, this operation is an involution:
combinat::skewPartitions::conjugate([[3, 2, 2, 1], [1, 1]])
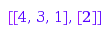
Example 3:
The "jacobiTrudy" function compute the Jacobi-Trudy matrix, see Macdonald I.-G., (1995), "Symmetric Functions and Hall Polynomials", Oxford Science Publication.
combinat::skewPartitions::jacobiTrudy([[4, 3, 1], [2]])

combinat::skewPartitions::jacobiTrudy([[4, 3, 1], [2]], T)

Example 4:
This example shows how to compute the corners of a skew partition.
combinat::skewPartitions::innerCorners([[4, 3, 1], [2]])

combinat::skewPartitions::outerCorners([[4, 3, 1], [2]])
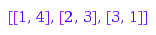
The inner and outer corners can be represented graphically:
combinat::skewPartitions::printPrettyCorners([[4, 3, 1], [2]])
+---+
| * |
+---+---+---+
| x | | * |
+---+---+---+---+
| x | * |
+---+---+
Sometimes inner and outer corners coincide:
combinat::skewPartitions::printPrettyCorners([[4, 3, 1], [3]])
+---+
| * |
+---+---+---+
| x | | * |
+---+---+---+---+
| % |
+---+
Or we can prefer a more compact representation:
combinat::skewPartitions::printPrettyCorners(
[[9, 8, 4, 3, 1], [6, 4, 3, 1]])
+---+
| % |
+---+---+---+
| x | * |
+---+---+---+
| % |
+---+---+---+---+---+
| x | | | * |
+---+---+---+---+---+
| x | | * |
+---+---+---+
combinat::skewPartitions::printCompactCorners(
[[9, 8, 4, 3, 1], [6, 4, 3, 1]])
%
x*
%
x##*
x#*
![]() of size
of size ![]() is a pair of two partitions
is a pair of two partitions ![]() where
where ![]() is a partition of the integer
is a partition of the integer ![]() ,
, ![]() is a partition of the integer
is a partition of the integer ![]() ,
, ![]() is an inner partition of
is an inner partition of ![]() and
and ![]() . We say that
. We say that ![]() and
and ![]() are respectively the outer and inner partitions of
are respectively the outer and inner partitions of ![]() .
.![]() which are not in the inner partition
which are not in the inner partition ![]() appear in the picture. For example, this is the diagram of the skew partition [[5,4,3,1],[3,3,1]]:
appear in the picture. For example, this is the diagram of the skew partition [[5,4,3,1],[3,3,1]]: 
